Adaptive reuse of buildings refers to the practice of repurposing existing structures for new uses rather than demolishing them and constructing new buildings. This approach to urban development and sustainability has gained popularity for several reasons:
Preservation of Cultural and Architectural Heritage
Adaptive reuse of building-2024

Preservation of Cultural and Architectural Heritage: Many old buildings have historical and architectural significance. Adaptive reuse allows these structures to be preserved and integrated into contemporary urban landscapes, maintaining a connection to the past.
Sustainability

Sustainability: Retrofitting existing buildings often requires fewer resources and generates less waste compared to new construction. Adaptive reuse reduces the environmental impact associated with demolishing old buildings and constructing new ones.
Cost-Effectiveness

Cost-Effectiveness: In many cases, adaptive reuse can be more cost-effective than building from scratch. Repurposing an existing structure may require less initial investment and can often result in faster project completion times.
Community Revitalization
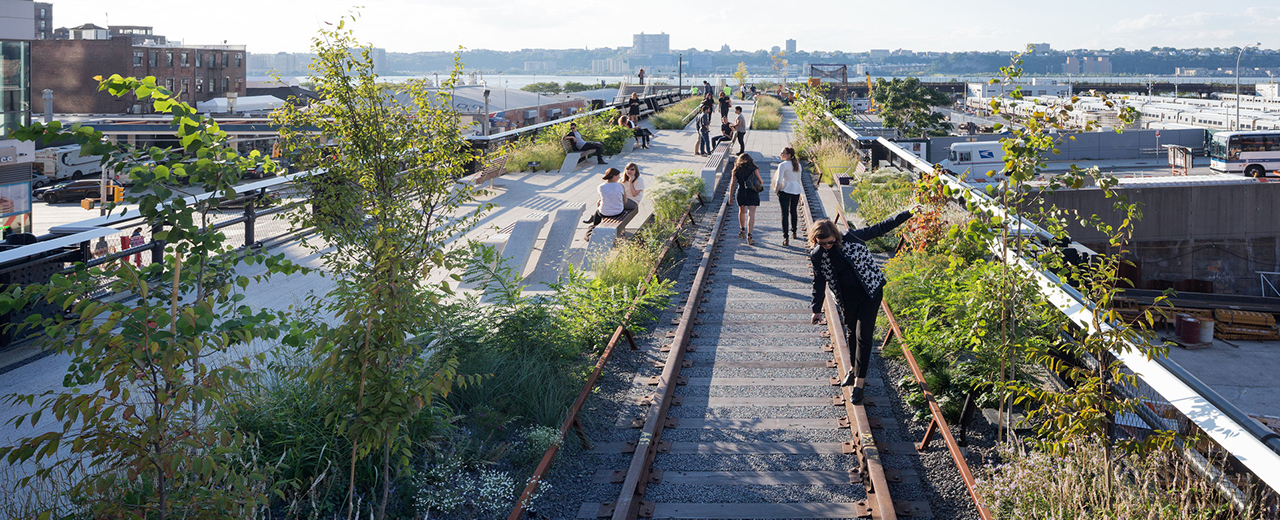

Community Revitalization: Converting old buildings into new, functional spaces can contribute to the revitalization of neighborhoods and downtown areas. Adaptive reuse projects can attract businesses, residents, and visitors, fostering economic growth and community development.
Flexibility and Creativity
Flexibility and Creativity: Existing buildings come with unique characteristics and features that can inspire creative design solutions. Adaptive reuse projects often involve innovative approaches to space utilization and design, resulting in dynamic and interesting environments.
Mixed-Use Development
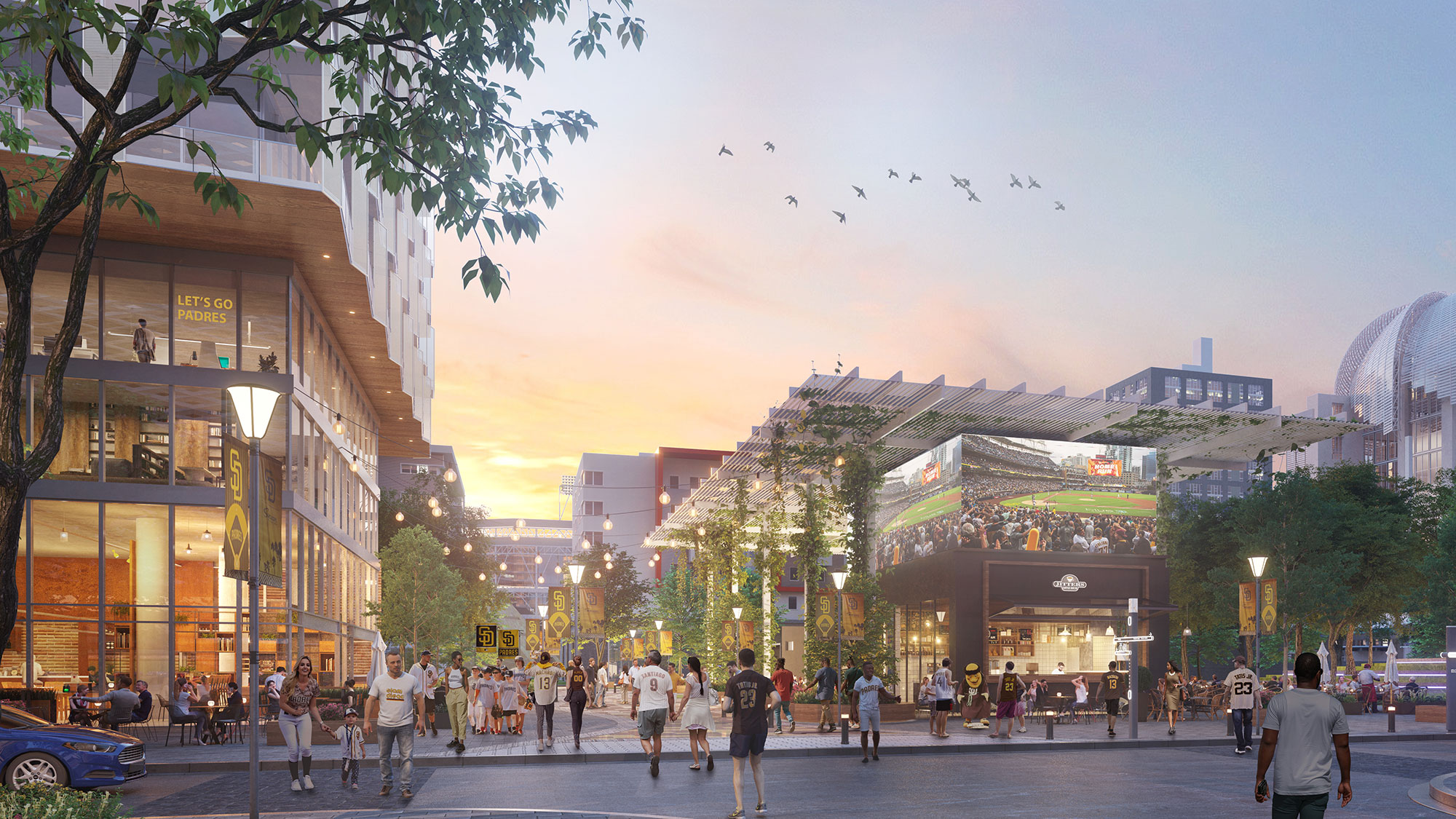

Mixed-Use Development: Adaptive reuse projects often result in mixed-use developments, where buildings serve multiple functions such as residential, commercial, cultural, or recreational purposes. This mixed-use approach fosters diverse and dynamic urban environments.
Regulatory Challenges

Regulatory Challenges: Despite its benefits, adaptive reuse can present regulatory challenges related to zoning, building codes, and historic preservation requirements. Navigating these regulatory frameworks requires collaboration between developers, architects, preservationists, and government agencies.
Structural and Technical Considerations

Structural and Technical Considerations: Before undertaking an adaptive reuse project, thorough structural assessments and feasibility studies are necessary to ensure the safety, integrity, and suitability of the building for its new purpose. Renovations may involve addressing issues such as structural stability, accessibility, and environmental sustainability.
Historic Preservation
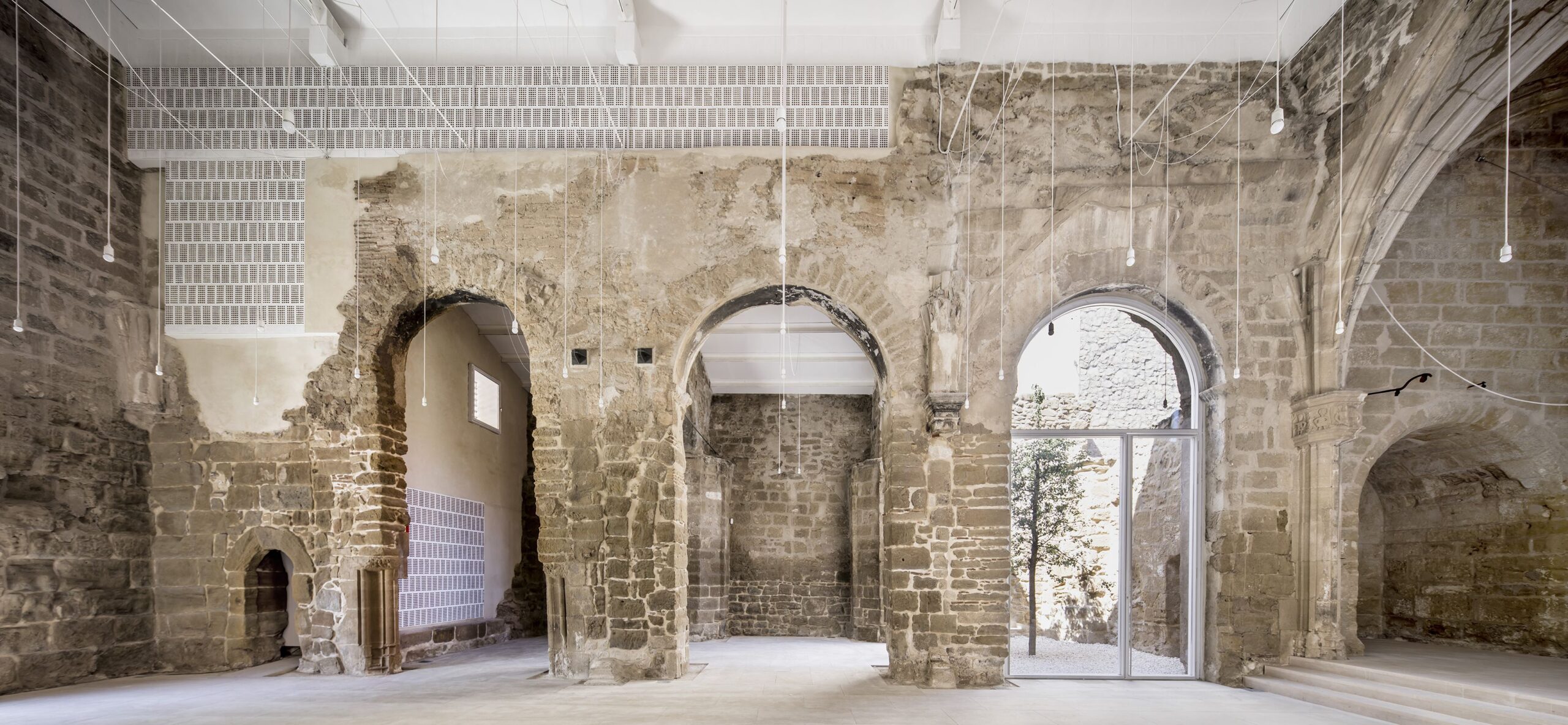

-
- Maintaining Cultural Heritage: Adaptive reuse helps preserve the cultural and historical significance of old buildings, allowing communities to retain a connection to their past.
- Architectural Value: Repurposing historic structures can showcase unique architectural features that may be lost through demolition.
-
Environmental Sustainability
-
-
Environmental Sustainability - Reduced Construction Waste: Adaptive reuse minimizes the need for new construction and reduces the amount of waste generated compared to demolishing and building from scratch.
- Energy Efficiency: Existing buildings often have durable materials and construction techniques, providing a foundation for energy-efficient upgrades and renovations.
-
- Economic Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Adaptive reuse can be more cost-effective than new construction, as the basic structure is already in place.
- Job Creation: Renovating existing buildings generates jobs in construction, design, and related industries, contributing to local economic development.
- Community Revitalization:
- Preserving Character: Repurposing old buildings can help maintain the character and charm of neighborhoods, contributing to a sense of place and community identity.
- Mixed-Use Development: Adaptive reuse often involves creating mixed-use spaces, such as combining residential, commercial, and cultural functions within a single building.
- Flexibility and Creativity:
- Adaptable Spaces: Existing structures can be transformed to meet modern needs without compromising their structural integrity.
- Innovative Designs: Designers and architects can showcase creativity in adapting buildings for new purposes, resulting in unique and inspiring spaces.
- Challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Zoning and building codes may present challenges when repurposing buildings, requiring creative solutions and collaboration with local authorities.
- Structural Concerns: Assessing and addressing structural issues is crucial to ensure the safety and longevity of the repurposed building.
Examples of adaptive reuse projects include transforming old factories into residential lofts, converting warehouses into office spaces or art galleries, and repurposing churches or schools into community centers or event venues.
While adaptive reuse offers many benefits, it also presents challenges such as addressing structural integrity, complying with building codes and regulations, and managing potential environmental hazards such as lead paint or asbestos. However, with careful planning, collaboration between stakeholders, and innovative design solutions, adaptive reuse can contribute to more sustainable and vibrant cities.


good information