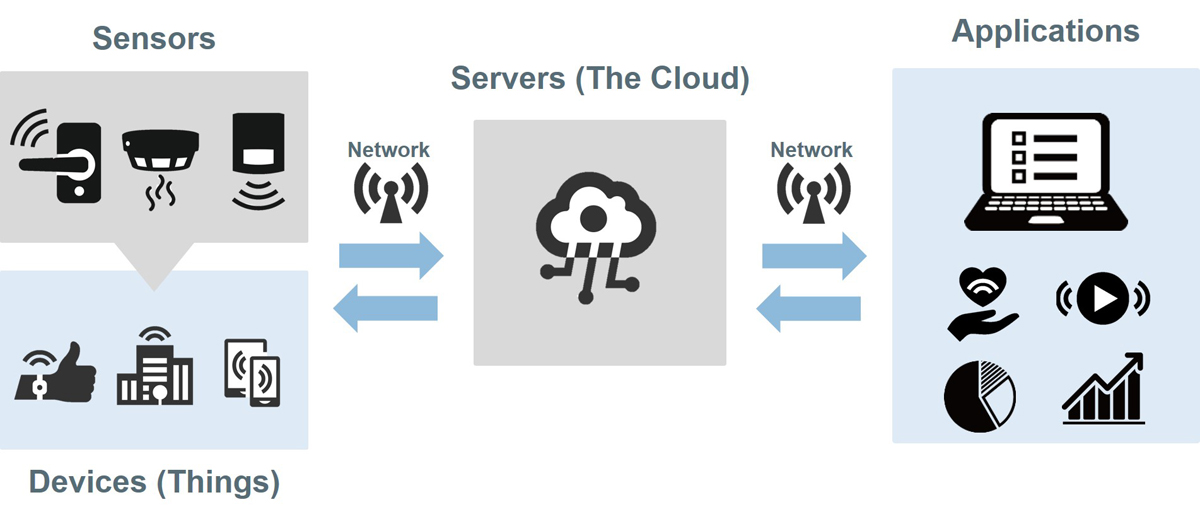
A “smart building-2025” refers to a structure that incorporates various automated processes to control and manage its operations effectively. These buildings leverage advanced technology and connectivity to optimize energy efficiency, enhance security, improve comfort, and streamline maintenance. Key components of a smart building include:
IoT Devices
- IoT Devices
IoT Devices: Smart buildings are equipped with a network of interconnected Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as sensors, actuators, and controllers. These devices collect data on various aspects of the building’s environment, including temperature, lighting, occupancy, air quality, and energy usage.
Building Management Systems (BMS)
-
Smart building-2025 Building Management Systems (BMS): BMS or Building Automation Systems (BAS) serve as the central control hub for monitoring and managing the building’s systems and processes. They integrate data from IoT devices and enable automated control of heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, and other systems.
-
Data Analytics
-
Data Analytics -
Data Analytics: Smart buildings-2025 utilize data analytics software to analyze the vast amount of data collected from sensors and other sources. These analytics provide insights into energy consumption patterns, occupant behavior, equipment performance, and maintenance needs, enabling building operators to make informed decisions and optimize building performance.
-
Energy Efficiency
-
Energy Efficiency: One of the primary goals of smart buildings is to minimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs. Energy management systems and smart meters help track energy usage in real-time, identify inefficiencies, and implement strategies such as demand response, predictive maintenance, and optimized scheduling to conserve energy.
Automation and Control
-
Automation and Control Automation and Control: Automation plays a crucial role in smart buildings, enabling tasks such as automatic lighting adjustments based on occupancy levels, temperature regulation, predictive maintenance alerts, and remote monitoring and control of building systems via mobile or web-based interfaces.
-
Integration and Interoperability
-
Integration and Interoperability Integration and Interoperability: Smart buildings often involve the integration of diverse systems and technologies from multiple vendors. Interoperability standards and protocols ensure seamless communication and compatibility between different components and systems, facilitating efficient operation and management.
-
User Experience
-
- User Experience
User Experience: Smart buildings aim to enhance the occupant experience by providing comfortable and productive indoor environments. Features such as personalized climate control, adjustable lighting, occupancy-based room scheduling, and mobile apps for facility management contribute to a more convenient and user-friendly experience for building occupants.
-
Building Automation Systems
-
Building Automation Systems (BAS): BAS is a central control system that manages and monitors the building’s mechanical, electrical, and security systems. It helps optimize energy usage, improve occupant comfort, and streamline facility management.
Sensors and IoT Devices
-
Sensors and IoT Devices Sensors and IoT Devices: Smart buildings incorporate a network of sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to collect data on temperature, humidity, lighting, occupancy, and other parameters. This data is used to make informed decisions for energy efficiency and space utilization.
-
Energy Management
-
Energy Management Energy Management: Smart buildings focus on energy conservation and sustainability. They often integrate energy-efficient HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, smart lighting solutions, and renewable energy sources to reduce the environmental impact and operational costs.
-
Intelligent Lighting
-
Intelligent Lighting : Automated lighting systems adjust based on occupancy, natural light levels, and time of day. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to a more comfortable and productive environment for occupants.
-
Security and Access Control
-
Security and Access Control : Smart buildings deploy advanced security systems such as biometric access control, surveillance cameras, and intrusion detection. These systems can be integrated with the overall building management for a comprehensive security solution.



 Energy Efficiency: One of the primary goals of smart buildings is to minimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs. Energy management systems and smart meters help track energy usage in real-time, identify inefficiencies, and implement strategies such as demand response, predictive maintenance, and optimized scheduling to conserve energy.
Energy Efficiency: One of the primary goals of smart buildings is to minimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs. Energy management systems and smart meters help track energy usage in real-time, identify inefficiencies, and implement strategies such as demand response, predictive maintenance, and optimized scheduling to conserve energy.